Dust Control for Powder Handling

All powder handling and processing within a manufacturing process has the potential to generate dust in the atmosphere of the facility where the powder handling equipment is housed. Minimizing dust levels well below hazardous and explosive levels is important to avoid loss of life, injuries and lost plant, equipment and money. Dust control for powder handling is important. Examples? The CSB (US Chemical Safety Board) made an exhaustive study and published recommendations. The first of three major recommendations made by the CSB is “Control Fugitive Dust Emissions.”
A must-read for all particulate processors and handlers:
- NFPA 654 Standard for the “Prevention of Fire and Dust Explosions from the Manufacturing, Processing and Handling of Combustible Dust Particulate”.
- NFPA 652 Standard on the “Fundamentals of Combustible Dust”.
- OSHA “Combustible Dust: An Explosion Hazard”.
Dry material weighing systems, Micro, Minor and Bulk batching systems, and Bulk Bag Filling / Bulk Bag Unloading systems all can generate dust within the atmosphere in your facility and should be evaluated for whether they need dust control for powder handling. While these systems are not the cause of any known dust hazard incidents, it is important to minimize or eliminate their contribution of dust to prevent any hazard, including the hazard of the existence of toxic dust, not just explosive dust. So how do we do this?

Each Sterling Systems & Controls, Inc. material weighing, micro, minor, and bulk batching system and bulk bag filling or unloading system is custom-engineered for safety as well as to meet your exact application requirements. Dust control for powder handling is important, let’s see what we can do to assist you in making sure your material weighing (micro, minor and bulk) systems and bulk bag handling systems are not contributing to a problem. The industries where dust explosions are more likely to occur include Food, Pharmaceutical, Wood Products, Chemical Processing and Metal Processing. In material weighing or batching systems, there are generally two places where dust can escape into the atmosphere, e.g. Discharge Points from Feeders and at the Filling Point of Supply Bins. Let’s see how we deal with these:
Feeder Discharge Points
Two types of feeders are routinely used in material weighing systems, most often the screw or auger feeder is used. However, it is not uncommon to use vibratory feeders. The Sterling Systems & Controls ACCU-PORTION™ Micro, Minor and Bulk batching systems and the general industry Material Weighing Systems use the Sterling Systems & Controls manufactured screw/auger feeders as standard. For high accuracy systems, the vibratory type feeder may be used, especially where the weighment is Micro (under 50lbs/23kg) in size.
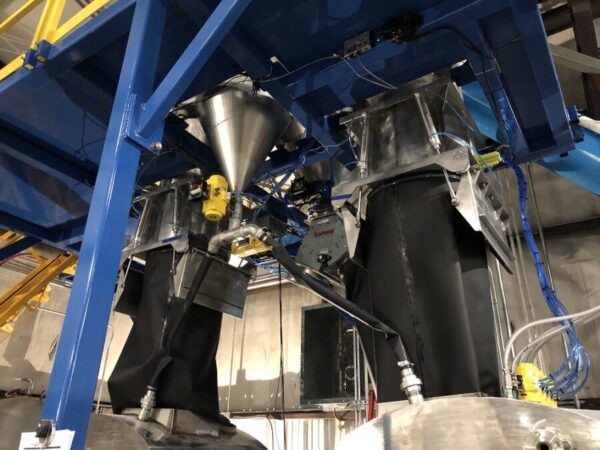
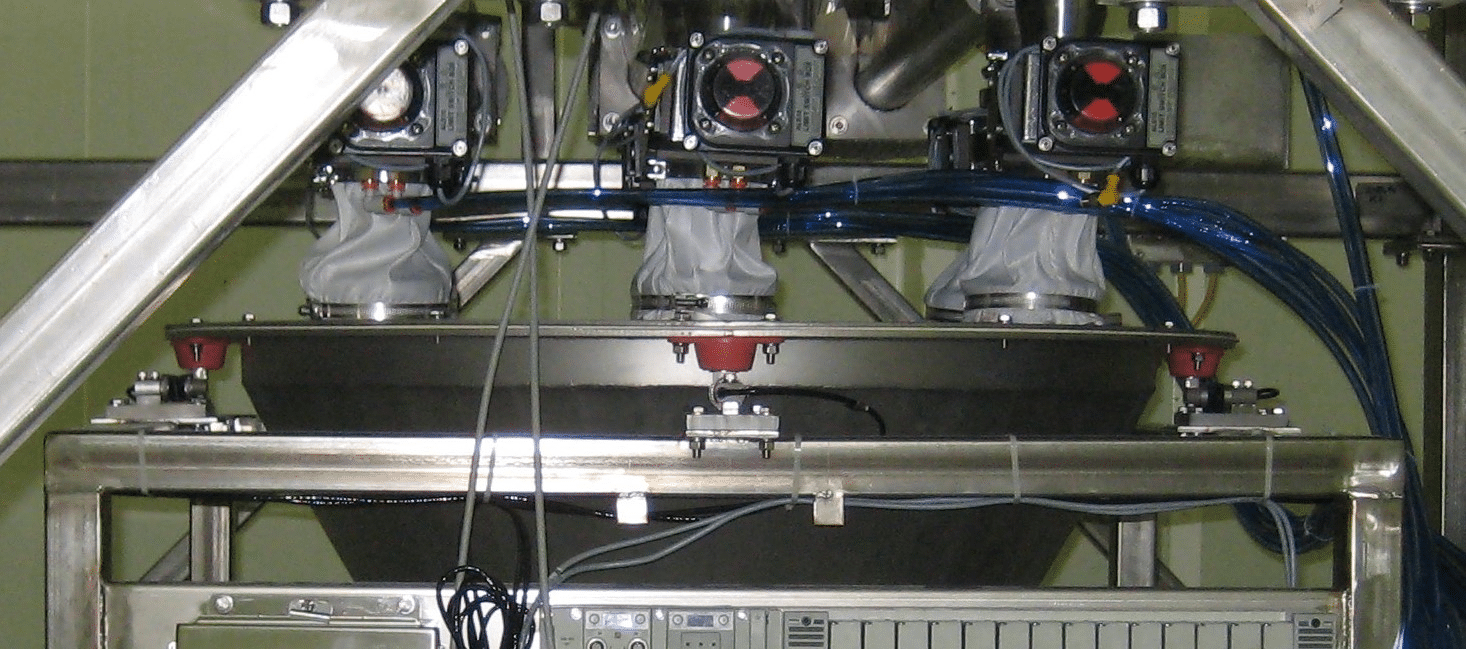
The methods used for dust control with Screw/Auger feeders depend on the mode of batch collection and takeoff. If the takeoff method is by conveyor, pneumatic or drag, the batches are collected in scale hoppers. Sterling Systems & Controls routinely and uniquely uses multiple scale hoppers to increase throughput, accuracy and customer profitability. Dust control when using screw/auger feeders that discharge into one or more scale hoppers is accomplished by using sealed top hoppers and “feeder socks” (Figure 2). A feeder sock is flexible and secured at the top (feeder) and bottom (scale hopper), and made of Nylon Satin material. This allows for a flexible connection between the feeder and hopper, and eliminates potential dust during the ingredient batching process. Generally speaking, 5 or 6 ingredients will be collected in a single scale hopper (but that can vary and be less or more depending on system performance requirements).
The pneumatic and mechanical methods of conveyance from scale hoppers downstream are sealed as well. A typical pneumatic conveying takeoff is shown in Figure 1.
When vibratory feeders are used the feeder tray is provided with a cover, and feeder and bin dust socks are also used. The picture in Figure 3 illustrates this. In this installation, the vibratory feeders are used to provide very high accuracy of a small micro weighment into a large traveling tote. Dust collection is also utilized in this case because of the traveling tote. The vibratory feeders discharge through a feeder hood that is also a dust collector hood. This brings us to the next item for discussion, Dust Collection.
When the material weighing system or micro/minor/bulk batching system collects the batches and weighed material in a traveling tote, a dust collection system is often required, especially if the dust is deemed to be explosive, toxic, or capable of accumulating to fuel any possible secondary explosion. This need can exist with small totes and large totes. The experience and skill of a dust collection system manufacturer is needed to ensure the system is properly sized and engineered to be 100% effective. Proper maintenance is also required to dispose of collected dust and to ensure the system is cleaned and maintained in good working order at all times.
An example of a dust collector used with a material weighing system (micro, minor or bulk) is shown in Figure 5. This particular dust collector is used in conjunction with a minor ingredient batching system in a food application. This system collects dust during the ingredient discharge and batch collection process and supply bin refills. In another photo (Figure 4) the arrows point to dust collection hoods above the supply bins and above traveling totes that collect the batches. When properly designed and maintained these dust collection systems will help eliminate dust control problems.
Bulk Bag Filling or Unloading Systems
Many powders are packaged, sold and shipped in large bags. They are called “bulk bags“. They are also known by other names, such as FIBC’s (flexible intermediate bulk containers). A piece of process equipment known as a bulk bag unloader or bulk bag discharger is used to remove or unload the powder or bulk material from the bag. When dealing with the removal of powder materials from bulk bags we have the potential for dust to be introduced into the facility atmosphere. The design of the bulk bag unloading system can be such that dust is minimized or eliminated at the discharge point. This is accomplished most often by using a dust containment box and other components such as an iris valve and connection to a dust collection system. The photo in Figure 6 shows a bulk bag unloading system with a containment box.
