Food and Baking Automation: Enhancing Quality and Consistency
In today’s fast-paced food and baking industries, staying ahead means focusing on efficiency, quality, and consistency to drive brand loyalty and a solid, profitable business. Automation has become a critical and necessary asset due to the increasing demand for raw agriculture-based ingredients, rising consumer expectations, and complex regulations. Automating key food process areas like ingredient batching, process control, and overall process automation are making a significant impact. Let’s explore how advancements in these areas are shaping the future of food production (for human and animal consumption) and why they matter to you, the process engineer, operations professional, and nutritionist in the food, pet food, and animal feed industry sectors.
Modern Ingredient Batching: Streamlining Production
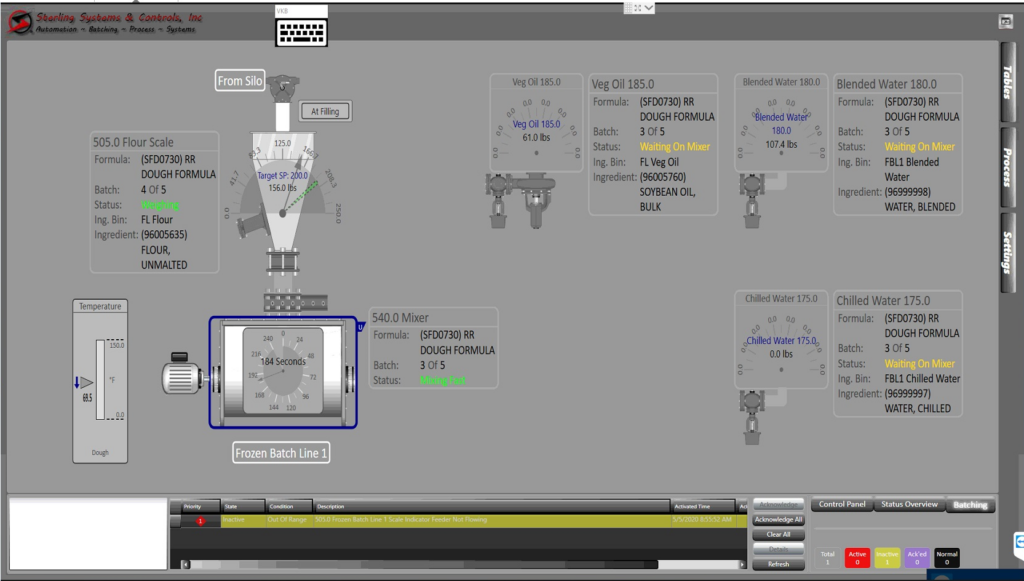
Ingredient batching is a core part of food, baking, and pet food processes, where precise measurement and mixing of ingredients are crucial for producing consistent, high-quality products. Traditionally, these tasks were performed manually, often leading to inconsistencies and inefficiencies that could affect the final product. Operators had to carefully measure and mix ingredients by hand, which was time-consuming and susceptible to human error. As production demands and quality expectations have increased, the need for more reliable and efficient batching solutions has become evident. Today, advanced technologies have transformed ingredient batching with both automatic and semi-automatic systems, offering significant improvements. These systems streamline the process while enhancing ingredient measurement accuracy, ensuring product consistency, driving brand loyalty, and addressing many of the challenges associated with manual batching.
Automatic Ingredient Batching Systems
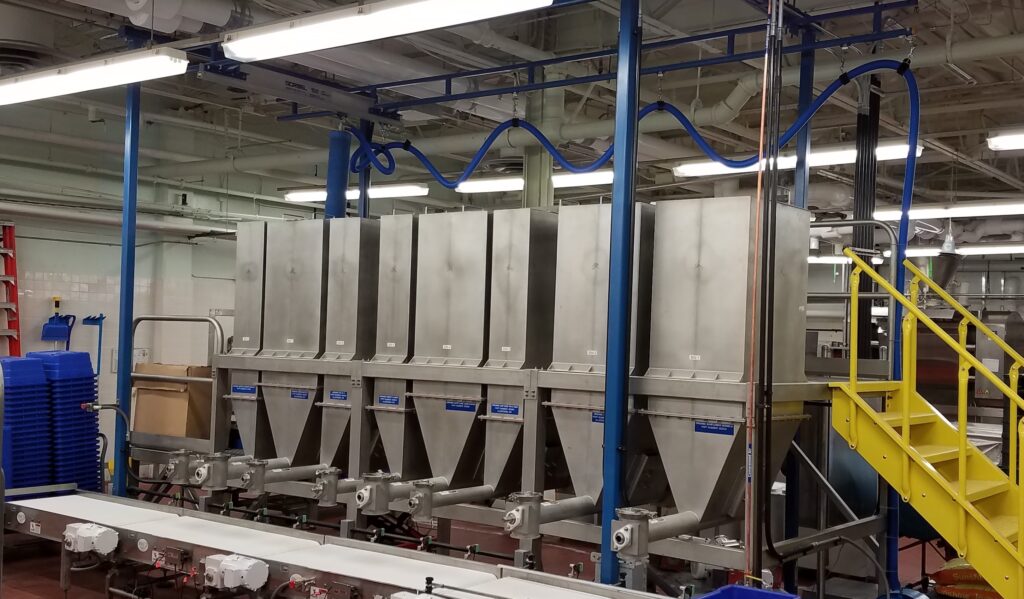

Automatic batching systems take the guesswork out of ingredient measurement and mixing by automatically feeding each ingredient into batch containers such as individual batch container totes or weigh scale hoppers. Using advanced sensors and software, these food processing automation systems ensure that every ingredient is added in the right amount, by weight, and in the correct sequence. For example, in a bakery, an automatic batching system can manage flour, sugar, yeast, and other ingredients weighments into a batch simultaneously, ensuring that each batch of dough or batter is consistent and accurately representative of the chosen recipe.
Semi-Automatic Ingredient Batching Stations
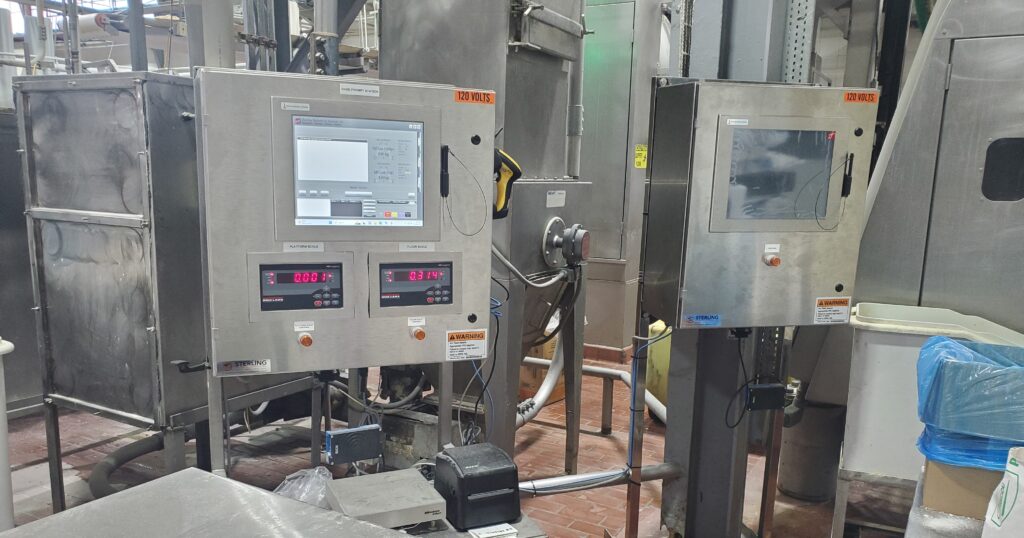

For operations looking for a practical middle ground between manual batching and complete automatic ingredient batching, semi-automatic batching stations offer a practical solution. These stations combine manual ingredient feeding with automated functions to precisely control operator actions, enhancing accuracy and efficiency. Typically, operators are involved in setting up the system and overseeing the ingredient addition process, while the semi-automatic batching station handles the precise weight measurement and inclusion of the correct ingredients required to complete a recipe.
Semi-automatic batching systems typically feature user-friendly operator interfaces that allow your employee to input recipes, feed each ingredient into the batch collection container, and monitor batching in real-time. While these semi-automatic systems still require human intervention, they significantly reduce the manual effort involved in measuring and mixing, and eliminate the weighment measuring errors and missed ingredients associated with manual batching. This approach can be particularly useful for smaller production facilities or those transitioning from manual to fully automated systems. Semi-automatic batching systems include the hand-prompt batching station and the kitchen batching system, including ingredient storage bins and worktables.
Why Automation Matters
- Accuracy: Automated systems, whether semi-automatic or automatic, eliminate human error in weighing ingredients, ingredient inclusion, and even the required actions that ensure ingredient traceability is possible. This means precise measurements, consistent results, and enhanced brand loyalty.
- Efficiency: Automatic ingredient batching systems are great examples of food processing automation. These systems speed up production and increase processing power in terms of production capacity, allowing for larger volumes and faster turnaround to grow with increasing future demand. In this case study an existing system was modified to increase production capacity ten-fold while substantially reducing the manual handling of batch mixing bowls. Read Here.
- Consistency: Automation ensures that each batch of a recipe meets the same high standards time after time, batch after batch. This is crucial for maintaining product quality, which can drive ever increasing consumer trust.
- Cost Savings: Reduced waste and increased efficiency translate into lower production costs and better profitability.
- Data Management: The amount of data gathered during your processing functions can be substantial. To take advantage of this, consider ensuring that the automated process control systems collect and manage your data using open programming languages such as Microsoft SQL and SQL Express. Even when adopting entry-level semi-automatic systems, a SQL database can evolve and grow as you expand from semi-automatic to fully automatic systems. The data integration to your ERP for further use and analysis is also essential.
The Power of Process Control
Effective process control is crucial for maintaining food products’ quality and consistency. Advanced process control systems play a pivotal role in this by continuously monitoring and adjusting production parameters, ensuring that every aspect of the manufacturing process runs smoothly and meets established standards.
Advanced Process Control Systems
Modern food processing automation control systems leverage real-time data to manage key variables such as temperature and mixing times. For instance, in a bakery, precise temperature control is essential for achieving the perfect texture and color in baked goods. These systems provide the capability to fine-tune processes, ensuring that every batch meets the desired specifications and quality standards time and time again. This produces product consistency that consumers expect and demand.
Benefits of Process Control
- Quality Assurance: By continuously monitoring and adjusting production parameters, advanced process control systems help maintain consistent product quality and minimize deviations, ensuring that every product meets high standards.
- Preventative and Predictive Maintenance: These systems are equipped to monitor process machinery and proactively schedule and perform maintenance to ensure downtime is minimized, scheduled, or eliminated. It may also be possible to predict failures and take actions to prevent unscheduled downtime and safety problems, as well as predict potential equipment issues before they become critical, allowing for proactive preventative maintenance.
- Regulatory Compliance: Automated process control aids in adhering to industry regulations and standards, facilitating smoother audits and inspections by ensuring consistent compliance. Automation also allows for data collection regarding ingredient uses, lots, and inventory in automatic ingredient batching systems. These systems can integrate data with ERP systems for further predictive trend analysis. Automation process systems can also provide remote browser-based supervisory control functions.
- Operational Efficiency: Automation systems for food processing can provide real-time data analysis, enabling the optimization of production processes, enhancing overall efficiency, reducing waste, and maximizing resource utilization.
By implementing advanced process control systems, manufacturers can significantly enhance the reliability and efficiency of their food processing operations, ultimately leading to better quality food products and improved operational performance.
Comprehensive Process Automation
Beyond batching and process control, automation impacts many aspects of production. From raw material handling to baking, dryer monitoring and control, specialty food process functions, packaging, and the addition of other automation technologies like robotics and data analytics, which are beginning to help transform food processing and baking operations.
Robotics in Production
Robotic systems are increasingly taking over packaging, palletizing, automatic depanners, and quality inspection tasks. Vision and camera systems and robots handle repetitive and strenuous tasks with precision, freeing up human workers for more complex roles. For instance, robots can efficiently package bread in a bakery, ensuring each loaf is wrapped and labeled correctly.
Data Analytics and IIoT
Integrating data analytics and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) offers valuable insights into production performance. Companies can identify trends, optimize processes, and make informed decisions by analyzing data from various stages of the baking and food process. Data gathered can be integrated with your ERP where advanced analytics can reveal inefficiencies in food processing automation equipment, batching or other processes, allowing for improvements that boost productivity.
Why Embrace Comprehensive Automation?
- Enhanced Productivity: Comprehensive food processing automation significantly accelerates production processes, allowing businesses to keep pace with increasing consumer demands and market pressures. Companies can boost output, streamline operations, and efficiently manage higher production volumes by automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks. This increased productivity not only meets current demands but also positions companies to adapt to future growth opportunities swiftly.
- Improved Quality: Automation ensures consistency and precision in production processes, which leads to higher-quality products. Automated systems maintain strict control over critical variables such as temperature, mixing ratios, and processing times by standardizing operations and minimizing human error. This level of precision helps achieve uniform product quality, reduce defects, and enhance overall reliability, leading to greater customer satisfaction and fewer quality issues.
- Reduced Labor Costs: Implementing automation can substantially lower labor costs by reducing the need for manual intervention. Automated systems take over routine and repetitive tasks, allowing employees to focus on more strategic and value-added activities. This reduction in manual labor not only decreases direct labor expenses but also minimizes the costs associated with training, errors, and potential workplace injuries.
- Scalability: One of the key advantages of automation is its scalability. Automated systems are designed to easily adjust to varying production needs, whether scaling up to meet increased demand or scaling down during quieter periods. This flexibility ensures that businesses can efficiently respond to market changes, optimize resource use, and maintain operational agility in a dynamic environment. As a result, companies can better align their production capabilities with market fluctuations and strategic goals.
Embracing comprehensive automation drives operational efficiency and positions businesses for long-term success by enhancing productivity, quality, and flexibility while controlling costs.
Key Considerations for Implementing Automation
- System Integration: Ensure new automation technologies integrate well with your existing systems to avoid disruptions.
- Training and Support: Train, Train, and Train. Invest in staff training and ongoing support to ensure smooth operation and maintenance of automated systems.
- Cost vs. Benefit: Evaluate the initial investment against long-term benefits like efficiency, reduced labor costs, and improved quality. When looking at ROI, aim for positive directional ROI rather than an arbitrary number.

Conclusion
Automation in raw material storage and movement, ingredient batching, mixing, classifying, baking, drying, other process control functions, and overall production is transforming the food and baking industries. Adopting these technologies means improved quality, consistency, and efficiency for process engineers, operations professionals, and nutritionists. Automated systems streamline production, ensuring that each product meets high standards and helping businesses stay competitive.
As the industry evolves, keeping up with automation advancements will be crucial for achieving success and meeting market demands. Whether you’re involved in food processing, baking, or pet food manufacturing, automation offers exciting opportunities to elevate your operations and achieve new levels of efficiency and quality.
Next Step
With over 50 years of expertise in custom engineering material weighing, ingredient batching, liquid handling, process control, and other bulk material handling solutions for the baking, food processing, pet food, and other consumer goods industries, Sterling Systems & Controls proudly has the experience to assist you in achieving your automation and process control goals and requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our knowledge and experience can align with your goals and how you can continue your journey toward manufacturing excellence!